Pre-requisites
- OpenJDK8
- Zookeeper
Install OpenJDK
|
Make sure you have the right OpenJDK version
|
It should display 1.8.0_111
Set JAVA_HOME
|
Building Apache Zookeeper
Download and unzip the Zookeeper package from Official Apache archive in all machines that will be used for zookeeper quorum as shown below:
$ tar -xzvf zookeeper-3.4.12.tar.gz |
Edit the /etc/hosts file across all the nodes and add the ipaddress and hostname (nodenames).
|
Create zookeeper user
|
Configure zookeeper
Now, Create the directory zookeeper under /var/lib folder which will serve as Zookeeper data directory and create another zookeeper directory under /var/log where all the Zookeeper logs will be captured. Both of the directory ownership need to be changed as zookeeper.
$ sudo mkdir /var/lib/zookeeper $ cd /var/lib $ sudo chown zookeeper:zookeeper zookeeper/ $ sudo mkdir /var/log/zookeeper $ cd /var/log $ sudo chown zookeeper:zookeeper zookeeper/ |
Edit the bashrc for the zookeeper user via setting up the following Zookeeper environment variables.
$ export ZOO_LOG_DIR=/var/log/zookeeper |
Source the .bashrc in current login session:
$ source ~/.bashrc |
Create the server id for the ensemble. Each zookeeper server should have a unique number in the myid file within the ensemble and should have a value between 1 and 255.
In Node1
$ sudo sh -c "echo '1' > /var/lib/zookeeper/myid" |
In Node2
$ sudo sh -c "echo '2' > /var/lib/zookeeper/myid" |
In Node3
$ sudo sh -c "echo '3' > /var/lib/zookeeper/myid" |
Now, go to the conf folder under the Zookeeper home directory (location of the Zookeeper directory after Archive has been unzipped/extracted).
$ cd /home/zookeeper/zookeeper-3.4.13/conf/ |
By default, a sample conf file with name zoo_sample.cfg will be present in conf directory. Make a copy of it with name zoo.cfg as shown below, and edit new zoo.cfg as described across all the nodes.
$ cp zoo_sample.cfg zoo.cfg |
Edit zoo.cfg and the below
$ vim /home/zookeeper/zookeeper-3.4.13/conf/zoo.cfg |
|
Now, do the below changes in log4.properties file as follows.
$ vim /home/zookeeper/zookeeper-3.4.13/conf/log4j.properties |
zookeeper.log.dir=/var/log/zookeeper zookeeper.tracelog.dir=/var/log/zookeeper log4j.rootLogger=INFO, CONSOLE, ROLLINGFILE |
After the configuration has been done in zoo.cfg file in all three nodes, start zookeeper in all the nodes one by one, using following command:
$ /home/zookeeper/zookeeper-3.4.13/bin/zkServer.sh start |
Zookeeper Service Start on all the Nodes.
The log file will be created in /var/log/zookeeper of zookeeper named zookeeper.log, tail the file to see logs for any errors.
$ tail -f /var/log/zookeeper/zookeeper.log |
Verify the Zookeeper Cluster and Ensemble
In Zookeeper ensemble out of three servers, one will be in leader mode and other two will be in follower mode. You can check the status by running the following commands.
$ /home/zookeeper/zookeeper-3.4.13/bin/zkServer.sh status |
Zookeeper Service Status Check.
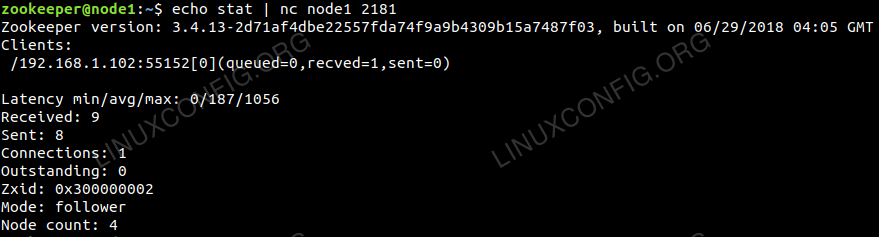
$ echo stat | nc node1 2181 |
Lists brief details for the server and connected clients.
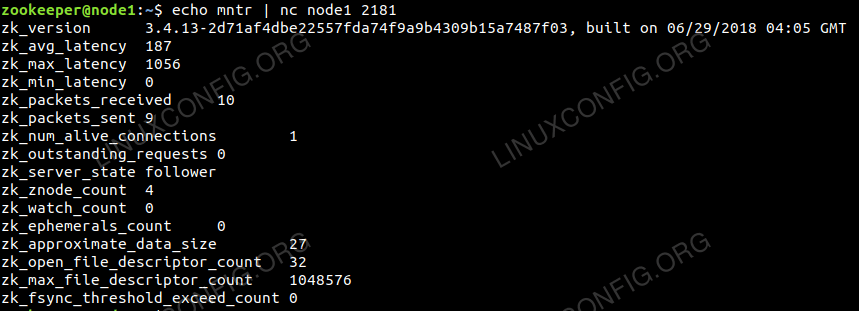
$ echo mntr | nc node1 2181 |
Zookeeper list of variables for cluster health monitoring.
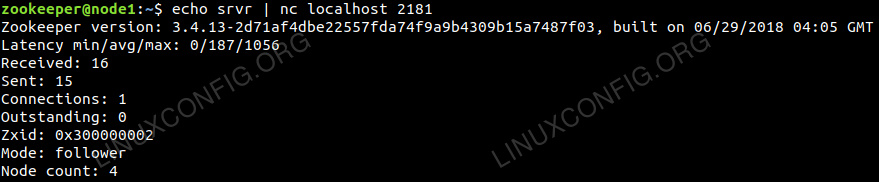
$ echo srvr | nc localhost 2181 |
Lists full details for the Zookeeper server.
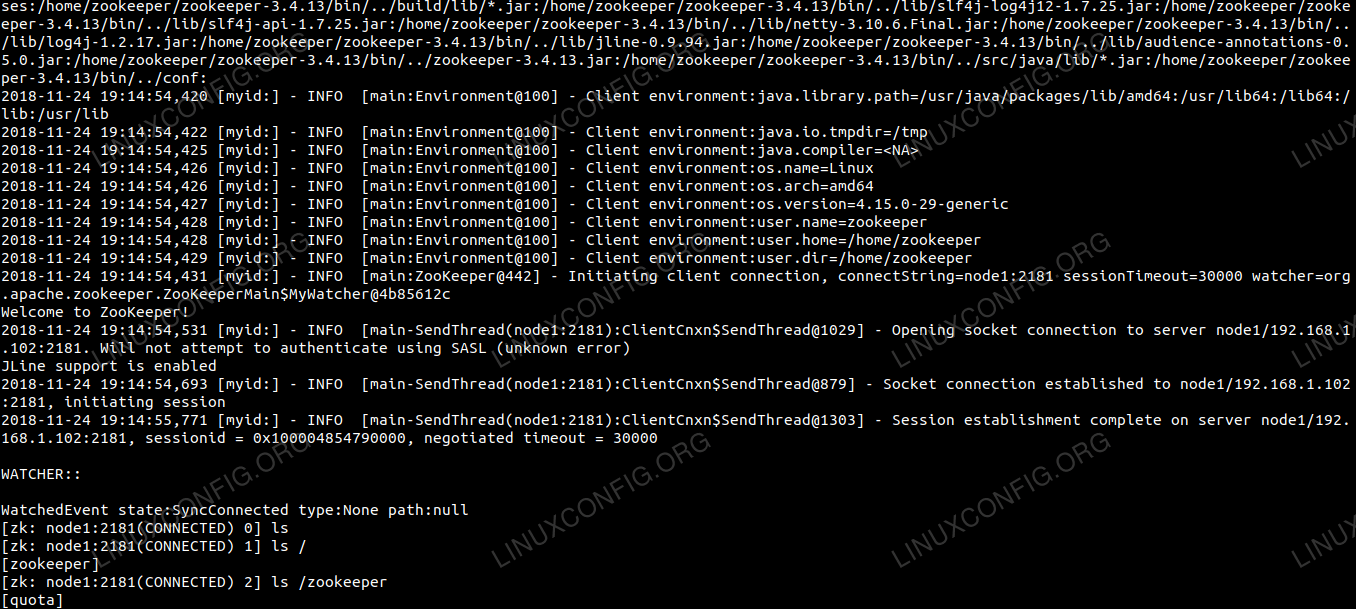
If you need to check and see the znode, you can connect by using the below command on any of the zookeeper node:
$ /home/zookeeper/zookeeper-3.4.13/bin/zkCli.sh -server `hostname -f`:2181 |
Connect to Zookeeper data node and lists the contents.